
CBD oil is made from hemp. But is CBD oil the same as hemp oil?
Well, it doesn’t have to be.
Hemp oil can refer to various different products, one of them being CBD oil. But it can also refer to other types of products.
And some of the products called ‘hemp oil’ don’t contain any CBD.
For example:
When you want to try CBD, the last thing you want is buy hempseed oil.
Hempseed oil is one of those products sometimes called ‘hemp oil’ that doesn’t have any CBD.
After reading today’s post you’ll exactly understand what you’re buying when you buy any product with ‘hemp’ or ‘CBD’ inside the name.
Let’s get started.
Table of Contents
What Is CBD Oil?
CBD oil is an umbrella term for any oil that contains CBD.
Generally CBD oil comes in three different forms:
- full-spectrum,
- broad-spectrum, and,
- isolate.
Full-spectrum CBD Oil Is a Complete Extract From Hemp Plants Combined with a Carrier Oil
‘Full-spectrum’ in ‘full-spectrum CBD oil’ means that it contains the ‘full-spectrum’ of cannabinoids that are found in hemp plants.
Besides CBD, the hemp plant contains other cannabinoids like:
- CBC,
- CBCA,
- CBG,
- CBGA,
- CBDV,
- CBDA,
- THC,
- THCA,
- THCV
Studies have identified over 70 different cannabinoids inside cannabis plants (1). Hemp is a variety of the cannabis plant species.
And these are just cannabinoids.
Hemp plants have many other active compounds as well, including:
- over 120 different identified terpenes,
- at least 23 different identified flavonoids.
Terpenes are the compounds that give cannabis and hemp strains their unique smell. And flavonoids are a different type of plant compounds with unique beneficial effects.
A true full-spectrum CBD oil should also have some terpenes and flavonoids present.
In practice though, if a CBD oil contains other cannabinoids than CBD, including THC, it gets labeled with ‘full-spectrum’.
Because raw or distillated hemp extract is extremely concentrated and doesn’t get absorbed very well by your body, it’s always combined with a carrier oil like MCT oil.
Cannabinoids are fat-soluble. This means they’re only properly absorbed inside your body when they’re taken with fats. They only dissolve in fats, not in water. And to be properly absorbed by your body they need to be dissolved.
Now, this is important:
Because a true full-spectrum CBD oil is complete extract from the hemp plant, sometimes it’s also called ‘hemp oil’.
So ‘hemp oil’ can sometimes refer to full-spectrum CBD oil.
Broad-spectrum CBD Oil Is a Complete Extract From Hemp Plants Without THC, Combined with a Carrier Oil
Broad-spectrum CBD oil is similar to full-spectrum CBD oil. Besides CBD, it contains other hemp compounds, with one major difference:
It’s always free from THC.
But because the THC gets filtered out, the quality of the extracts suffers. Other hemp compounds get filtered out unintentionally as well.
Because a broad-spectrum oil is technically still an extract from the hemp plant, some brands call their broad-spectrum CBD oil things like:
- ‘broad-spectrum hemp oil’,
- ‘THC-free hemp oil’,
- or even just ‘hemp oil’.
So ‘hemp oil’ can sometimes refer to broad-spectrum CBD oil.
Of course, a broad-spectrum CBD oil also always comes with a carrier oil to reduce concentrations and improve bioavailability.
CBD Isolate Oil Is Purified CBD Combined with a Carrier Oil
CBD isolate oil is always CBD crystals or powder dissolved in a carrier oil.
Purified CBD crystals and powders are created by completely purifying a hemp extract from everything except CBD.
As explained, cannabinoids like CBD are fat-soluble. So to improve bioavailability, this purified CBD then gets dissolved in a carrier oil.
A CBD isolate oil doesn’t resemble the hemp plant it came from in cannabinoids or terpenes.
It literally is CBD dissolved inside a carrier oil.
You now know that the hemp plant contains hundreds of other compounds.
A CBD isolate oil doesn’t contain any of these other compounds.
It would be a stretch to call CBD isolate ‘hemp oil’. Out of hundreds hemp compounds, it literally only contains one: CBD.
Yet, some brands call their CBD isolate oil ‘hemp oil’.
The bottom line:
Whatever we think is a true ‘hemp oil’ isn’t very relevant when brands can call any type of CBD product ‘hemp oil’.
So a bit further in the article, you’re going learn how to exactly identify what type of product any product called ‘hemp oil’ is.
What Is Hempseed Oil?
To confuse things further, a lot of hempseed oils are labeled ‘hemp oil’ as well.
But what is hempseed oil exactly? Is it similar to CBD oil?
Hempseed oil Is Oil Pressed Out of Hemp Seeds
Hempseed oil has no relationship to the actual hemp plant.
It’s only made from the seeds.
The seeds from a hemp plant are fundamentally different from the plant.
The hemp plant has high levels of cannabinoids like CBD, and also terpenes and flavonoids. Hemp seeds barely contain any cannabinoids and definitely no terpenes.
They have a completely different chemical profile.
Hempseed oil contains high levels of essential fatty acids like linolenic acid and alpha-linolenic acid. Extract from hemp plants contains high levels of cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids.
Needless to say, hempseed oil doesn’t have any of the benefits that are associated with cannabinoids like CBD.
What Is True Hemp Oil?
There’s no universally accepted definition of ‘hemp oil’.
You now know that ‘hemp oil’ can refer to:
- full-spectrum CBD oil,
- broad-spectrum CBD oil,
- CBD isolate oil, or,
- hempseed oil.
But if you’re asking my opinion…
The label ‘hemp oil’ should only be given to true full-spectrum CBD oil.
Why? Because true full-spectrum CBD oil has a similar chemical profile as the hemp plant.
The plant is called ‘hemp’. So when you have oil called ‘hemp oil’, you would expect an oil that’s made from the hemp plant, not from the seeds of that plant. Nor would I expect it to be an oil with a single compounds from the hemp plant, like you would have with CBD isolate oil.
I think it’s extremely confusing that a lot of hempseed oil brands and CBD isolate oil brands call their product ‘hemp oil’.
Even broad-spectrum CBD oil, in my opinion, shouldn’t be called ‘hemp oil’.
But since I know these labels won’t easily change…
The following question needs an answer:
How to Know What You’re Buying?
The only way to truly determine what type of oil your ‘hemp oil’ is, is by checking the product’s certificate of analysis (COA).
If A Hemp Oil Product Is a CBD Product, It Should Have a COA Where the Tested Amount of CBD Is Visible
If you want to be sure that you’re getting a product with cannabinoids like CBD, you NEED a COA.
Without such a report, you have no idea what you’re taking.
So any time you see a product called ‘hemp oil’, check the lab-test report and verify that the product contains cannabinoids like CBD.
An example COA report of a full-spectrum CBD oil:
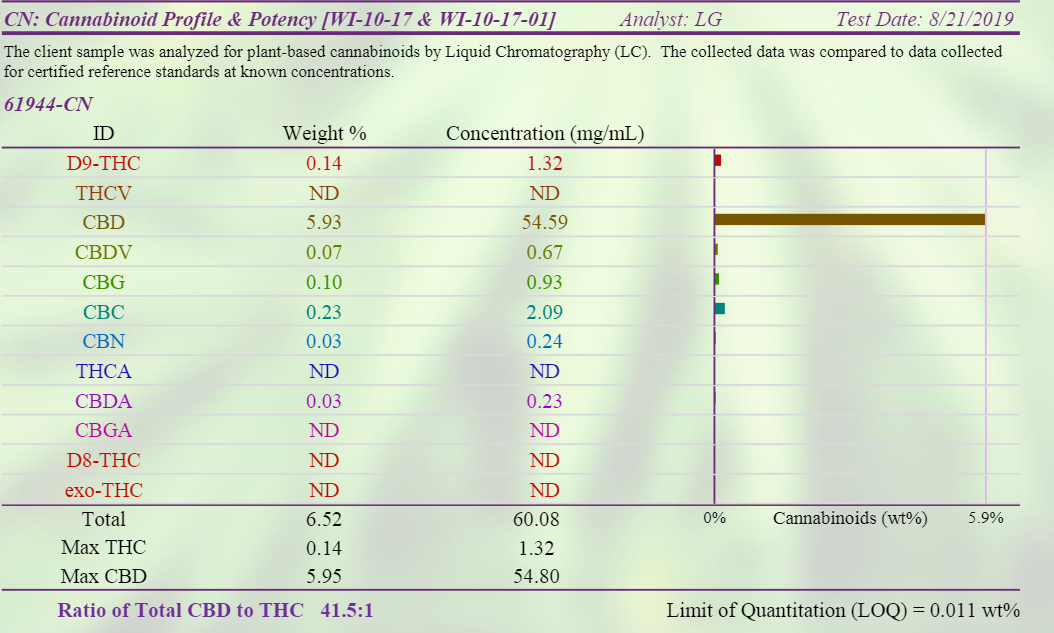
As you can see, this oil has high levels of CBD (5.93%) and also a good amount of other cannabinoids like CBG, CBC, and THC. This is a true full-spectrum CBD oil and worthy of the name ‘hemp oil’.
So if you find a hemp oil with a COA that shows:
- CBD > 1%,
- some minor cannabinoids, including THC,
know that it’s a full-spectrum CBD oil.
The lab-test report of a broad-spectrum CBD product can look similar to this, but it should always have 0% THC.
An example COA report of a broad-spectrum CBD oil:
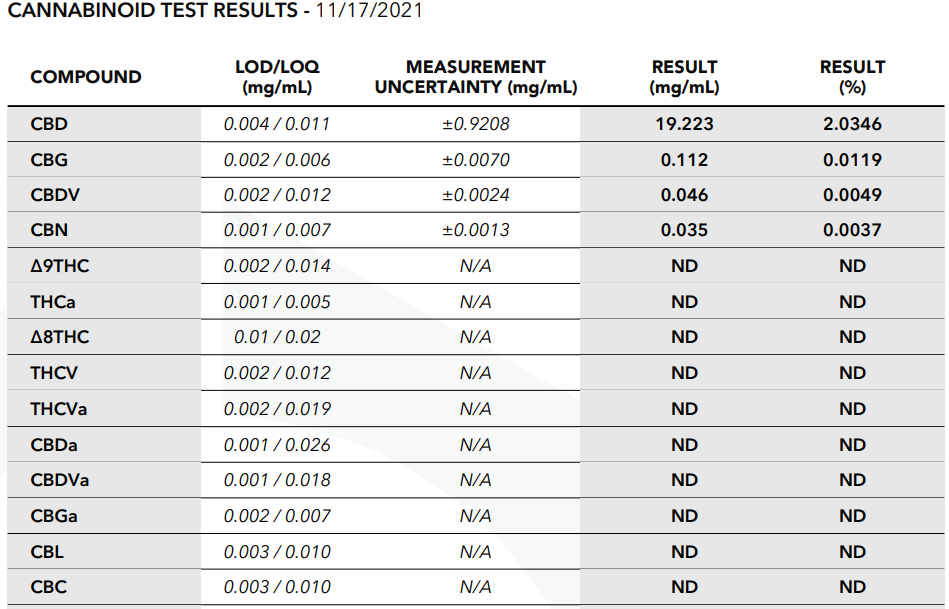
You can see that this oil contains a decent amount of CBD. A small amount of minor cannabinoids like CBG, CBDV, and CBN. But no THC at all.
You can also clearly see here that broad-spectrum CBD products usually have much lower levels of minor cannabinoids.
For example:
Compare the CBG-percentage of the full-spectrum CBD oil to the CBG-percentage of the broad-spectrum CBD oil: 0.1% vs 0.01%.
So if you find a hemp oil with a COA that shows:
- CBD > 1%,
- some minor cannabinoids,
- but no THC,
know that it’s a broad-spectrum CBD oil.
The lab-test report of a CBD isolate oil should only show CBD.
An example COA report of a CBD isolate oil:
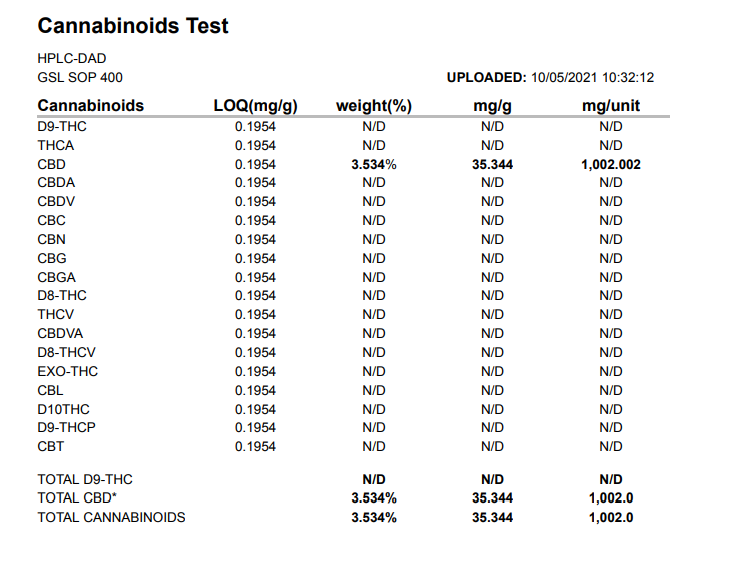
You can clearly see this oil contains only CBD and no other cannabinoids.
So if you find a hemp oil with a COA that shows:
- CBD > 1%, and,
- no minor cannabinoids,
know that it’s a CBD isolate oil.
The bottom line:
To verify whether your product labeled ‘hemp oil’ is a CBD product, you need to check its COA and verify that there’s actual CBD inside the product (> 1%).
If A Hemp Oil Product Is Hempseed Oil, It Should Have a COA Where the Fatty-Acid Profile Is Visible
High-quality hempseed oil brands also provide lab-test reports.
An example lab-test report of a hempseed oil product:
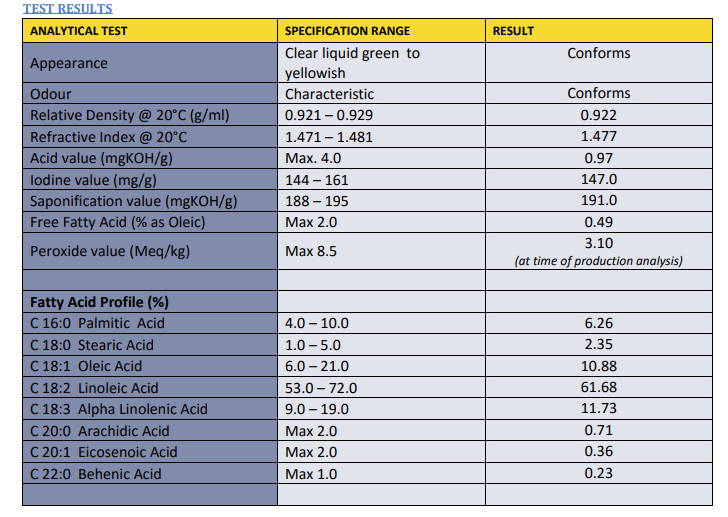
You can clearly see that this product has no cannabinoids like CBD. You also can clearly see the product’s fatty-acid profile.
With hempseed oils, one of the most important quality metrics is its fatty-acid profile. With CBD products, the fatty-acid profile isn’t important at all.
But a lot of hempseed oils don’t come with such a COA.
If a product is labeled ‘hemp oil’ and doesn’t have a COA, how do you know what kind of product it is?
Well, you should probably avoid such a product. Without a COA you never really know what you’re ingesting.
But there are a few other observable differences between hemp CBD products and hempseed oil products.
Although there are cheap CBD products, CBD oil is more expensive per milliliter than hempseed oil. Most CBD oils come in 30ml bottles.
Hempseed oil is significantly cheaper per milliliter and come in much larger bottles. For example, 500ml or 1000ml. A high-quality organic 500ml hempseed oil can already be bought for $12. 500ml of high-quality full-spectrum CBD oil would cost you more like $500. A significant difference in price.
So cost and bottle size are other to characteristics to differentiate between hempseed oils and hemp ‘plant’ oils.
Conclusion
Hemp oil can refer to:
- full-spectrum CBD oil,
- broad-spectrum CBD oil,
- CBD isolate oil, or,
- hempseed oil.
The only way to truly know what a product really is, is by checking the product’s certificate of analysis.
CBD products should contain cannabinoids like CBD, CBG, CBC, clearly visible on such a report.
Hempseed oil products should contain fatty acids like linolenic acid and alpha-linolenic acid.
If your product labeled ‘hemp oil’ doesn’t have a certificate of analysis, you should probably avoid taking it. Because you don’t really know what it is you’re ingesting without such a report.
What’s Next…
Go to our CBD Hub to learn more about CBD-related topics.
Scientific References:
- ElSohly, M. A., & Slade, D. (2005). Chemical constituents of marijuana: The complex mixture of natural cannabinoids. Life Sciences, 78(5), 539–548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2005.09.011