
CBD oil and CBD tincture are names used interchangeably for CBD oil products.
But are these products the same?
Well, they can be. But they don’t have to be.
Today you’re going to learn when these products are the same. But also, why not all CBD oils are true tinctures.
Let’s get started.
Table of Contents
What Is a Tincture?
Herbal tinctures are some of the oldest medicines in the world.
Centuries ago, various cultures already understood that dissolving certain plants or herbs inside alcohol could make for potent natural remedies.
And that’s exactly what a tincture is:
A tincture is botanical material dissolved inside a solution containing alcohol.
Alcohol is a very effective solvent that can extract beneficial compounds out of plant material.
By extracting these plant substances, you can concentrate the active compounds.
Rather than having to take many grams of plant material to achieve a particular effect, a tincture is so concentrated that all you may need to experience the plant’s benefits, are a few drops.
For example:
One gram of hemp flower can contain 100 milligram CBD.

One milliliter of CBD tincture can contain 100 milligram CBD as well:
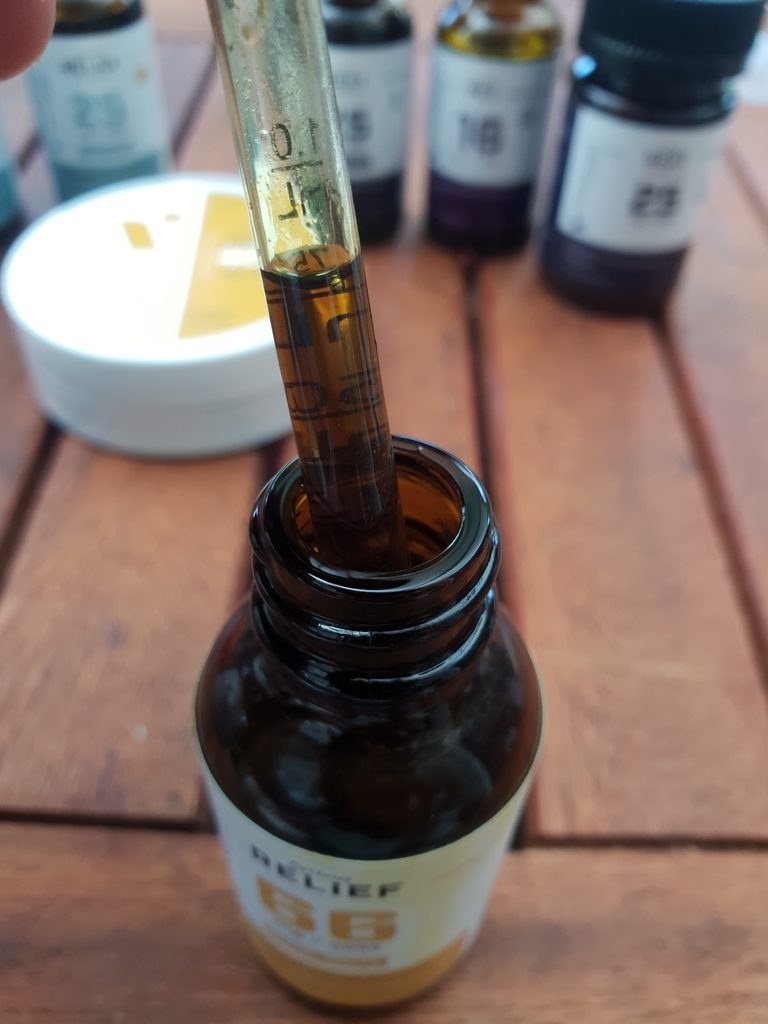

There’s a big difference in weight and volume between one gram and one milliliter.
One milligram of tincture is much less in weight and volume. So it’s much easier to consume than one gram of flower.
The other benefit of tinctures vs fresh or dried plant material is that the shelf life of properly stored tinctures is extremely long. When stored in a cool dark place, tinctures last for more than 5 years in some cases (1).
Some examples of ancient tinctures are:
- turmeric tinctures,
- milk thistle tinctures,
- valerian tinctures.
And while cannabis and hemp tinctures may seem like ‘new inventions’…
The truth is cannabis tinctures were used somewhat frequently as medicines in the 1800s for health issues related to pain, sleep and appetite (2).
But a cannabis tincture isn’t the same as a hemp or CBD tincture, as you’ll learn now.
What Is a CBD Tincture?
To understand what a CBD tincture is, first you have to understand the difference between ‘hemp’ and ‘marijuana’.
Both hemp and marijuana belong to the cannabis plant species. The difference is that hemp has low levels of THC, and generally high levels of CBD. While marijuana plants have high levels of THC and generally lower levels of CBD.
So a tincture made from marijuana plants generally has a lot of THC, but only a little CBD.
And a tincture made from hemp plants generally has a lot of CBD, but only a little THC.
When people talk about ‘cannabis tinctures’, they usually refer to tinctures made from marijuana plants. Meaning they contain a lot of THC, and only a little CBD.
So while technically a cannabis tincture can be a CBD or hemp tincture…
In practice, cannabis tincture refers to marijuana tincture.
Now:
Another key characteristic of tinctures is that they never contain isolated plant compounds. Since you’re dissolving whole plant parts inside a tincture, the tincture contains all compounds naturally present in the plant.
So a CBD tincture, by definition, contains more hemp compounds than CBD. So ‘CBD tincture’ and ‘hemp tincture’ can be used interchangeably.
That being said, there are various CBD brands that advertise their CBD isolate oil as ‘CBD tincture’. Factually this is wrong:
Why?
Because any CBD isolate product is made from purified CBD powder or crystal. And you just learned that a tincture is plant material dissolved in a solution with alcohol. Purified CBD crystals or powders are NOT plant material.
So any CBD isolate or purified CBD product is by definition NOT a tincture.
This also means that a tincture with only CBD doesn’t exist. By definition, a CBD tincture contains many hemp compounds. Using CBD tincture and hemp tincture interchangeably makes sense. But calling a product that only contains CBD, and no other hemp compounds a ‘tincture’, doesn’t make any sense.
So a CBD tincture is tincture containing hemp extract. It contains CBD, plus many other hemp compounds.
For example:
- other cannabinoids like CBG and CBC, or,
- terpenes like myrcene and linalool.
A true CBD tincture is always ‘full-spectrum’.
And various studies show that full-spectrum CBD products are more effective than products containing isolated CBD (3, 4).
What Is a CBD Oil?
CBD oil is an umbrella term for any oily solution that contains CBD.
In practice, most CBD oils are a concentrated hemp extract mixed with a carrier oil like MCT oil. And some of these hemp extracts are extracted with ethanol. In some cases, not all ethanol gets evaporated, and a little ethanol stays inside the extract. But in most cases, none of the ethanol stays inside the final product.
Whether any ethanol stays inside the final extract or not, most CBD oils that are labeled ‘tinctures’, simply are partially or fully extracted by means of ethanol-extraction.
But a CBD oil can also be a purified product, only containing CBD and no other hemp compounds.
A lot of CBD oils are also simply purified CBD powder or crystal dissolved inside a carrier oil like MCT oil.
So all CBD tinctures fall under the ‘CBD oil’ label. But not all CBD oils are true tinctures.
Tinctures are plant material dissolved inside a solution containing alcohol, or a solution with plant material that’s extracted with alcohol.
Again:
Purified CBD products are NOT made with plant material.
There are three types of CBD oils:
- full-spectrum,
- broad-spectrum, and,
- isolate.
contain CBD and many other hemp compounds. Some of these oils are correctly labeled as tinctures.
Broad-spectrum CBD oils contain CBD and some other hemp compounds, but are always free from THC. It’s debatable whether broad-spectrum CBD oils are correctly labeled tinctures. Why? Because hemp plants always contain some THC, if you filter out THC before you make the final product, the final product isn’t made with plant material, but with a derivative of the plant material. So it can’t really be called a tincture anymore.
CBD isolate oils are never made directly from plant material, so they can’t be called true tinctures either.
The only type of CBD oil that can be truly called a tincture, is one that’s made by means of either:
- dissolving hemp inside a solution containing alcohol, or,
- extracting hemp compounds directly from hemp plants with ethanol extraction.
By definition, these products are always full-spectrum.
That being said, many CBD brands falsely claim that their product is a ‘tincture’. So don’t be fooled by the advertising schemes.
How to Determine Whether a CBD Oil Is Truly a Tincture?
To determine this, you have to know the product’s:
- extraction method, and,
- what hemp compounds are inside the product.
Most CBD brands disclose their extraction method clearly on their website.
To see what hemp compounds are inside the product, you need a certificate of analysis (COA).
A true CBD tincture contains CBD, plus many other hemp compounds. And this should be clearly visible inside the (COA).
Let’s say you found out your CBD oil is the result of process that involves ethanol extraction.
You check the COA, and find the following:
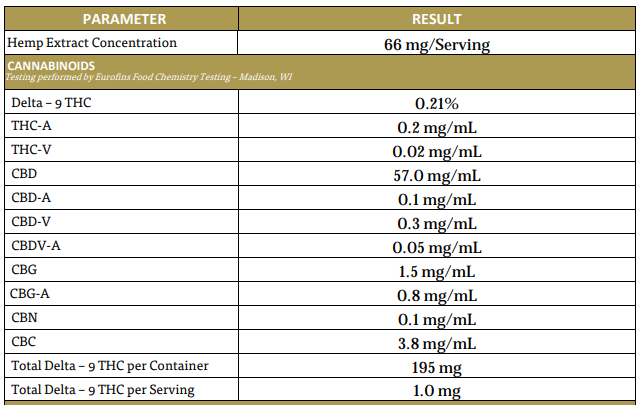
Besides, CBD, you see many other cannabinoids. This means it’s definitely a true tincture. These other cannabinoids wouldn’t be present if not the plant material was used.
Now:
Let’s say you found out your CBD oil is the result of process that involves ethanol extraction.
You check, the COA, but this time you see the following:
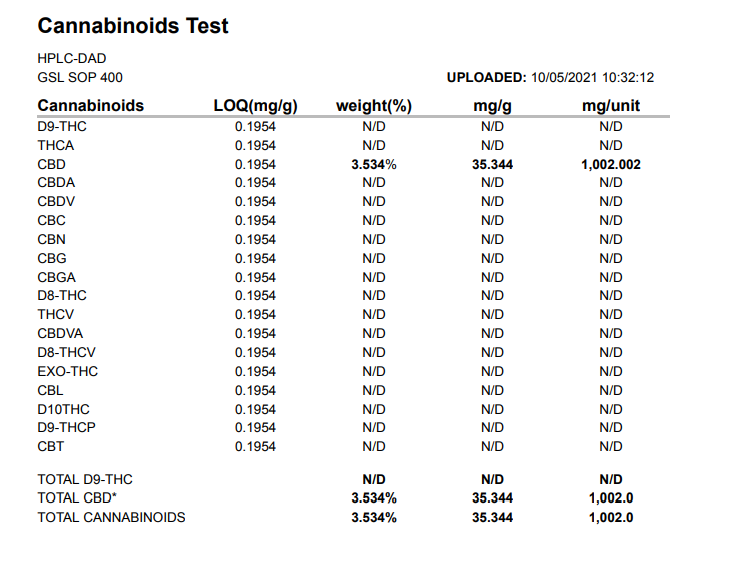
Your product contains no other cannabinoids than CBD.
This means it’s NOT a tincture.
Why?
Because if it was made from plant material, it would contain other cannabinoids in smaller concentrations.
The bottom line:
A true tincture contains many hemp compounds, not just CBD.
Conclusion
All CBD tinctures can be classified as CBD oils.
But not all CBD oils can be classified as tinctures.
A tincture is plant material dissolved in a solution containing ethanol.
When it comes to CBD the final tincture can be free from ethanol. But in that case the hemp compounds should have been extracted with ethanol for it to be truly classified as a tincture.
So a true CBD tincture is made by means of ethanol extraction and contains many other hemp compounds besides CBD.
CBD oil is an umbrella term for any oily substance that contains CBD. So it’s a much bigger category of products.
What’s Next…
Go to our CBD Hub to learn more about CBD-related topics.
Scientific Sources:
- Barve, R., & Kulkarni, S. (2014). Stability and Expiry Date of Remedies. Homoeopathic Links, 27(02), 110–114. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0034-1368361
- Zuardi, A. W. (2006). History of cannabis as a medicine: a review. Revista Brasileira de Psiquiatria, 28(2), 153–157. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1516-44462006000200015
- Pamplona, F. A., da Silva, L. R., & Coan, A. C. (2018). Potential Clinical Benefits of CBD-Rich Cannabis Extracts Over Purified CBD in Treatment-Resistant Epilepsy: Observational Data Meta-analysis. Frontiers in Neurology, 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2018.00759
- Maayah, Z. H., Takahara, S., Ferdaoussi, M., & Dyck, J. R. (2020). The molecular mechanisms that underpin the biological benefits of full-spectrum cannabis extract in the treatment of neuropathic pain and inflammation. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) – Molecular Basis of Disease, 1866(7), 165771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2020.165771