Although CBD products look similar on the surface …
Once you start to dig a little deeper, you’ll quickly learn there can be significant differences between them.
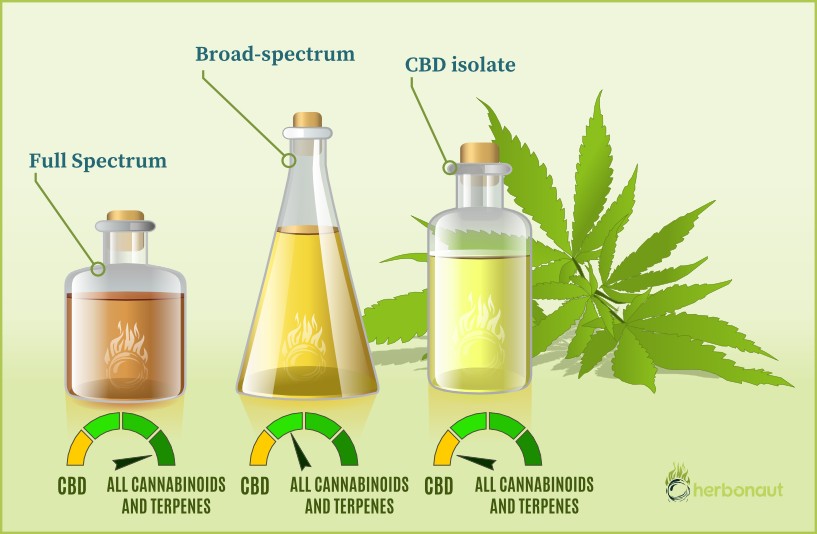
When we look at the differences between full-spectrum CBD oil vs. broad-spectrum CBD oil vs. CBD isolate, we can see huge differences in:
- The biochemical make-up of these products, and;
- The effects that each type of product produces.
Should you get a full-spectrum CBD oil, a broad-spectrum CBD oil or a CBD isolate product?
Today you’re going to learn about all the pros and cons of using one vs. the other.
CBD and the Entourage Effect
Both CBD isolate and full-spectrum oils come from hemp plants and both of them contain CBD. But that’s where the similarities end.
To learn about the differences between ‘cannabis’, ‘marijuana’, and ‘hemp’, read our beginner’s guide on what CBD oil exactly is.
A CBD isolate contains literally only CBD. A full-spectrum CBD oil contains many other hemp-derived compounds like:
- Other cannabinoids than CBD like THC, CBC, CBG, and;
- Terpenes like linalool, limonene, caryophyllene.
All these hemp-derived compounds have unique pharmacological effects and many of them are associated with unique health benefits.
But what’s even more important:
There are several studies that indicate that all these hemp-derived compounds can work together to enhance each other’s beneficial effects. This synergy between different hemp-derived compounds is called ‘the entourage effect’.
The first indication that cannabinoids and other cannabis-derived compounds could work together in a process called ‘the entourage effect’ was given in a study published in the European Journal of Pharmacology all the way back in 1998 (1).
In this study, researchers found that cannabinoid receptors would sometimes only get biologically activated when exposed to a specific combination of compounds. Individually, these compounds had no effect on the cannabinoid receptors, but together they could activate them.
More recently, a study published in the journal of Frontiers in Neurology, found that epilepsy patients using CBD-rich cannabis extracts reported using an effective dose of CBD that was 4-times lower than patients using purified CBD products (2).
Patients that used CBD-rich cannabis extracts also reported lower side effects like gastrointestinal discomfort or abdominal pain. This could, of course, be related to the lower doses of CBD that were associated with CBD-rich cannabis extracts.
The researchers note that CBD-rich cannabis extracts could be more potent and have a better side-effect profile than purified CBD products because they contain other cannabis-derived compounds that act synergistically to CBD.
CBD-rich cannabis extracts always contain high concentrations of CBD, but potentially also high concentrations of THC. Therefore these study results are not 100% relevant to commercially sold CBD oils that always contain a maximum percentage of 0.3% THC.
There are also studies that indicate that CBD could counteract the negative side effects of THC (3).
We can see that there’s a strong theoretical foundation backed by some evidence that:
- Cannabis-derived compounds influence each other’s effects in many different ways;
- CBD is more potent when taken together with other cannabis-derived compounds, and;
- CBD has a better side-effect profile when taken with other cannabis-derived compounds.
So when choosing between CBD isolate vs full-spectrum CBD products …
So should you always choose full-plant-extract/full-spectrum CBD oils?
Not necessarily.
To answer this question, let’s take a deeper look into the pros and cons of …
The Different Types of CBD Oils

Based on how the CBD oil is exactly manufactured, you can get biochemically very different products.
These are the factors that influence the biochemical composition of a CBD oil:
- Which strain of hemp is used for the extraction;
- Which parts of the hemp plant are used for the extraction, and;
- What extraction method is used for the extraction;
- What filtering process is used to create the final product, and;
- What decarboxylation process is used to convert CBDA into CBD.
Based on their biochemical composition, all CBD oils are sold under the following three (3) categories:
- Full plant extract/full-spectrum CBD oils;
- Broad-spectrum CBD oils;
- CBD isolate or purified CBD oils;
Let’s dive a bit deeper into these.
Full Spectrum/Full Plant Extracts CBD Oils

Full plant extract/full-spectrum CBD oils are as the name implies, an as complete as possible extract from the hemp plant, containing:
- A full spectrum of cannabinoids including other cannabinoids than CBD like CBC, CBG, THC (although in much lesser concentrations);
- A full spectrum of terpenes, and potentially also;
- Flavonoids;
- Vitamins, and;
- Other anti-oxidants naturally occurring in hemp plants.
A full plant extract CBD oil can be a CBD oil in its raw/crude form (the first unaltered extract from the plant). Usually, however, a full-plant extract CBD oil is a raw hemp-extract that has undergone a process of:
- Distillation or winterization, and;
- Decarboxylation.
A full plant hemp extract in its raw and unfiltered form is often extremely thick, sticky, and tastes bitter. There aren’t many sellers that sell these types of oil.
Most full-plant extract/full-spectrum CBD oils are distilled or winterized to remove:
- Waxes,
- Lipids, and
- Phosphides,
While keeping a full spectrum of cannabinoids and terpenes.
Full-Spectrum CBD Oil and the Entourage Effect
It’s thought that especially cannabinoids and terpenes have the most benefits when it comes to hemp-derived compounds.
Since a true full-spectrum CBD oil contains the full spectrum of cannabinoids AND terpenes of its source plant …
A full-plant extract makes the best case for the earlier-mentioned ‘entourage effect’.
To recap:
The entourage effect refers to the fact different hemp-derived compounds act synergistically to CBD to enhance its beneficial effects.
Now:
Since a true full-plant extract CBD oil should contain the full spectrum of cannabinoids and terpenes, PLUS in relatively high concentrations …
Full-spectrum CBD oil is best made from the flower parts of high-resin hemp plants.
Here’s why:
The resinous and trichome-rich flower of a hemp plant contains significantly more beneficial compounds than its stems and stalks.
True full-plant extract CBD oils are made from the flower of hemp plants that are:
- High-resin,
- Have a wide cannabinoid-profile and high cannabinoid content,
- Have a wide terpene-profile and high terpene-content, and;
- Preferably organically cultivated.
Full-spectrum CBD oils are closest to the source plant in their biochemical composition.
True full-spectrum/full-plant extract CBD oils are our preferred CBD oils because there’s some evidence backing up the idea that they are more potent and cause fewer negative side effects than purified CBD oils.
There are two potential downsides to using full-spectrum CBD oils:
- Since full-spectrum CBD oils don’t undergo an extensive filtering process, there’s a bigger chance of contaminants ending up in the final product.
- Full-spectrum CBD oils always contain some THC.
If you’re regularly subjected to drug tests, for example, you should avoid full-spectrum CBD oils. But you don’t have to worry that full-spectrum CBD products will produce psychoactive effects. The THC levels in full-spectrum CBD products are too low to produce psychoactive effects.
How you make sure you have a contaminant-free full-spectrum CBD oil is by only using CBD oils that are backed by 3th-party lab-test reports.
Classic example full-spectrum CBD oil:
To re-cap the pros and cons of full-spectrum CBD oil:
Pros:
- Closest to the original biochemical composition of hemp plants;
- Contains a wide variety of beneficial hemp-derived compounds;
- Makes the best case for the entourage effect, which refers to other hemp-derived compounds acting synergistically to CBD to enhance its beneficial effects;
Cons:
- To be contaminant-free, it’s essential that a full-spectrum CBD oil is made from clean hemp plants;
- Can’t use if you want to avoid THC (because of drug-tests for example).
Broad-Spectrum CBD Oils

Broad-spectrum CBD oils are in some ways similar to full-spectrum CBD oils:
Besides CBD, they can contain additional hemp-derived compounds like cannabinoids and terpenes.
But unlike full-spectrum CBD oil, broad-spectrum CBD oil doesn’t contain the full spectrum of cannabinoids and terpenes found in hemp plants. Broad-spectrum oils are usually THC-free.
Usually, a broad-spectrum CBD oil:
- Contains CBD;
- Is THC-free, and;
- Contains a few other cannabinoids and/or terpenes in low concentrations.
For example:
A full-spectrum CBD oil turns into a broad-spectrum CBD oil when it undergoes a process of distillation or winterization where some types of cannabinoids and/or terpenes get removed completely.
Or the CBD inside the raw hemp extract gets decarboxylated through a heating process and the terpenes evaporate.
Most ‘full spectrum’ CBD oils being marketed as such are in reality, broad-spectrum CBD oils.
Here’s why:
Keeping especially a full spectrum of terpenes inside the end-product is difficult and requires a very delicate manufacturing process from the moment a high-resin hemp plant gets harvested to the last step that’s involved in producing the end-product.
Terpenes are highly volatile compounds that not only evaporate very quickly but also degrade quickly if hemp isn’t handled and stored properly.
As explained before, most broad-spectrum CBD oils get advertised as ‘full spectrum’.
What some CBD sellers refer to as ‘full spectrum’, is just that their CBD oil contains other compounds extracted from the plant besides CBD …
But not necessarily the full spectrum of cannabinoids and terpenes (like you would have with a full-plant extract)!
Important to note here is that what CBD oil sellers usually mean with ‘broad-spectrum’ is that their CBD oil contains other cannabinoids besides CBD, but no THC.
A true full-spectrum CBD oil contains:
- The full spectrum of cannabinoids and terpenes found inside the resinous flower of hemp plants, and;
- Contains these in high detectable concentrations (not just trace elements).
A broad-spectrum oil contains:
- CBD, plus;
- A limited set of cannabinoids and/or terpenoids in, usually, low concentrations, and;
- Is THC-free.
To re-cap the pros and cons of broad-spectrum CBD oil:
Pros:
- Best option if you don’t want any THC, but still some other beneficial hemp-derived compounds;
- Best option if you don’t want any THC, but still want a chance to experience the entourage effect of CBD;
- Makes the best case for the entourage effect, which refers to other hemp-derived compounds acting synergistically to CBD to enhance its beneficial effects;
Cons:
- To be contaminant-free, it’s essential that a broad-spectrum CBD oil is made from clean hemp plants;
- If you’re ok with THC inside your oil, a full-spectrum CBD oil will generally be more potent.
Classic example broad-spectrum CBD oil:
Isolate/Purified CBD Oils

Isolate CBD oils are oils that only contain purified CBD and a carrier oil like olive oil or MCT oil.
Basically, you’re only getting CBD and nothing else. The source of a purified CBD product isn’t really important because:
The chemical make-up and quality of a CBD molecule are always the same. It doesn’t matter whether it comes from the flower of an organically cultivated high-resin hemp plant or from the stems and stalks of an industrially cultivated hemp plant. The quality of a CBD molecule is always the same.
If you’re going for a purified CBD product like a CBD isolate oil, just go for the cheapest you can find. Just make sure the carrier oil is of good quality.
The quality of the plants used to produce a CBD oil and the extraction method are most important when it comes to full-spectrum and broad-spectrum CBD oils.
In general, CBD isolate oils are cheaper than full-plant extracts or broad-spectrum oils, but also less potent because they won’t provide any of the aforementioned entourage-effect.
But here’s the deal:
If you want to test out CBD in its purest form (most CBD-related studies tested a purified form of CBD), this is the type of product you should get.
Getting the perfect dose each and every time will be slightly easier with a CBD isolate because there are no other hemp-derived compounds that influence CBD’s potency.
Also because CBD is the only active compound inside CBD isolate, it has fewer chances of interacting with other compounds like herbs and pharmaceutical drugs.
To re-cap the pros and cons of CBD isolate:
Pros:
- The quality of a CBD-molecule is always the same, which means that the source of CBD isolate isn’t that important in terms of contamination;
- Because CBD isolate can come from the stalks and stems of cheap industrial hemp plants, CBD isolate is generally cheap;
- Because the CBD inside CBD isolate doesn’t interact with other hemp-derived compounds, it’s the easiest the dose;
- Potential chances of other compounds like pharmaceutical drugs interacting with CBD isolate are smaller than with full-spectrum/broad-spectrum products, because these potential interactions are limited interactions with CBD;
Cons:
- There’s limited evidence indicating that CBD is more potent when taken together with other hemp-derived compounds;
- There’s limited evidence indicating that CBD has a better side-effect profile when together with other hemp-derived compounds;
The best CBD isolate products aren’t oils, but crystals and powders. CBD isolate crystals and powders offer much more CBD per dollar compared to oils.
Learn More
The Best CBD Oils: A list of our recommended CBD oils, includes full-spectrum CBD oils, broad-spectrum CBD oils, and CBD isolates. All are 3th-party lab-tested to confirm they’re contaminant-free and contain high levels of CBD.
The Best CBD Gummies: A list of our recommended CBD gummies. All are 3th-party lab-tested to confirm they’re contaminant-free and contain high levels of CBD.
The Best CBD Vape Oils: A list of our recommended CBD vape oils. All are 3th-party lab-tested to confirm they’re contaminant-free and contain high levels of CBD.
The Benefits of CBD Oil: A review of over 100 studies that found potential health benefits associated with CBD.
How to Use CBD Products: A review of over 40 studies that (among other things) looked at the effects and potency of CBD based on methods of use.
Scientific References:
-
Ben-Shabat, S., Fride, E., Sheskin, T., Tamiri, T., Rhee, M. H., Vogel, Z., . . . Mechoulam, R. (1998). An entourage effect: inactive endogenous fatty acid glycerol esters enhance 2-arachidonoyl-glycerol cannabinoid activity. European Journal of Pharmacology, 353(1), 23–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0014-2999(98)00392-6
-
Pamplona, F. A., da Silva, L. R., & Coan, A. C. (2018). Potential Clinical Benefits of CBD-Rich Cannabis Extracts Over Purified CBD in Treatment-Resistant Epilepsy: Observational Data Meta-analysis. Frontiers in Neurology, 9. Published. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2018.00759
-
Russo, E., & Guy, G. W. (2006). A tale of two cannabinoids: The therapeutic rationale for combining tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol. Medical Hypotheses, 66(2), 234–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2005.08.026